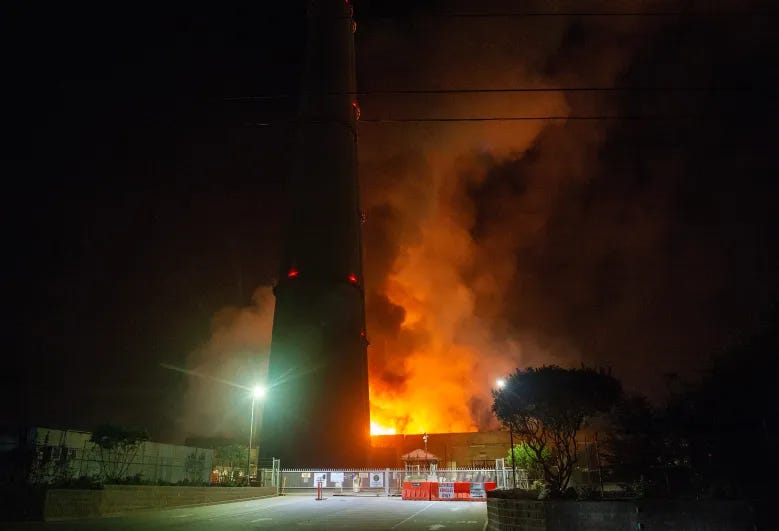
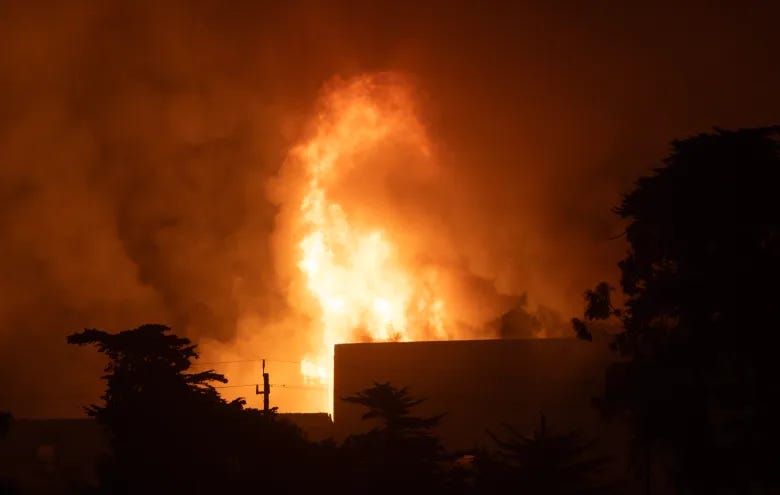
Fire at Moss Landing Fire battery plant flares again after officials earlier said ‘most of the fire is out.’ Evacuations and road closures continue. The facility has been the site of other fires before.
Fires broke out at the Vistra plant on Sept. 4, 2021, and Feb 14, 2022. Investigations showed that they were caused by a malfunction in a fire sprinkler system, which released water and caused several of the units to overheat.
Then in September 2022, a fire broke out at the PG&E Elkhorn battery plant. Police closed Highway 1 for 12 hours. An investigation found it was caused by an improperly installed vent shield on one of the 256 units, which allowed rainwater to get in and short out the batteries. There were no injuries to firefighters, PG&E employees or the public.
Afterward, Gov. Gavin Newsom signed a law requiring battery storage plants in California to draw up emergency response plans with local fire departments and increase fire safety. NFPA 855 is a standard from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) that establishes requirements for installing stationary energy storage systems (ESS). The standard covers the design, construction, installation, and maintenance of ESS. In California, storage battery regulations for power plants primarily focus on safety measures, including proper installation location, fire-resistant barriers, emergency response plans, and compliance with the California Energy Commission (CEC) standards, ensuring that battery systems meet specific performance requirements and are certified by the CEC; all overseen by the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) with specific rules outlined in the California Fire Code regarding outdoor storage placement and separation distances from buildings and public areas.
Key points about California storage battery regulations for power plants:
Safety focus:
The primary concern is ensuring battery storage facilities are designed and operated safely to prevent fire hazards, including proper ventilation, separation distances from combustible materials, and fire suppression systems.
Emergency response plans:
All battery storage facilities must have detailed emergency response plans that include coordination with local emergency management agencies and first responders.
California Energy Commission (CEC) standards:
Battery systems must meet the performance requirements outlined by the CEC and be certified by them.
California Fire Code requirements:
Installation locations for battery storage must comply with the California Fire Code, which specifies minimum distances from property lines, buildings, and public areas.
SB 38 legislation:
This California law mandates that all battery energy storage facilities have a comprehensive emergency response and action plan.
Where to find more information:
California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC):
The primary regulatory body overseeing energy storage systems in California.
California Energy Commission (CEC):
Provides information on battery storage system certification requirements and standards.
California Fire Code:
Contains specific regulations regarding the placement and installation of battery storage systems.
Battery Energy Storage Systems
High-rise multifamily buildings and some nonresidential building categories are prescriptively required to have a battery energy s...
California Energy Commission
California introduces fire safety rules around battery storage ...
Oct 17, 2023 — New legislation in California that requires battery storage facilities to put in place safety and communication protoc...
Energy-Storage.News
2022 High-rise Multifamily Battery Storage Systems
NOTE: The solar PV requirements still apply when exempted from battery storage. What are the Minimum Battery Storage Performance R...
California Energy Commission (.gov)
Show all
The adoption of solar energy requires storage to provide electrical power during high demand and at night when there is no sunlight.
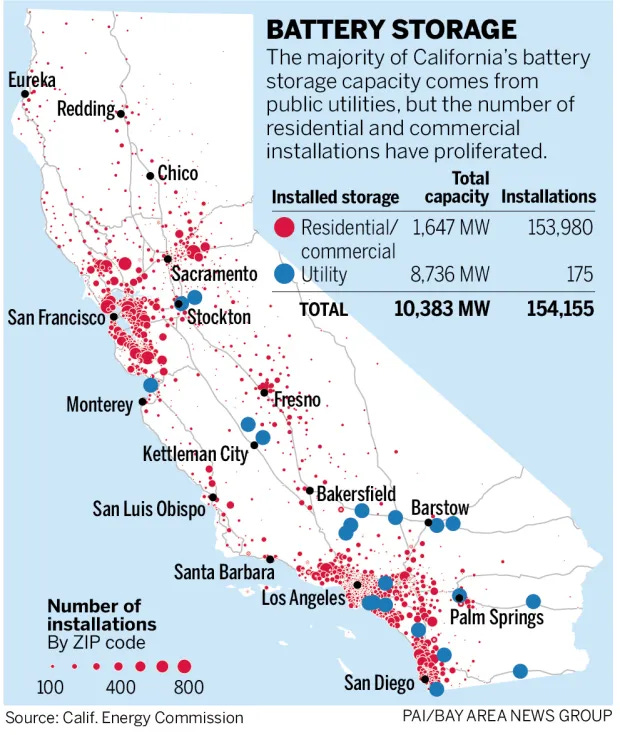
Battery storage has increased sevenfold in the past five years in California, from 1,474 megawatts in 2020 to 10,383 megawatts this past summer. A megawatt is enough electricity to run 750 homes.
The unregulated proliferation of battery storage units will far exceed the existing number of nuclear power plants.
Although solar energy is less polluting, storage batteries require huge amounts of lithium, an unstable element that explodes upon contact with water. Battery units create a thermal reaction and some batteries have been known to combust spontaneously.
A storage battery facility is a ticking time bomb. Intrusion of water, and unregulated temperatures are events that can start an uncontrollable fire. Toxic chemical byproducts and gasses can contaminate large areas rendering them unsafe for inhabitation and even transportation through the area.
Does that sound like Three Mile Island or Chornobyl in Ukraine?