The Evidence is in, and it supports the opinion of Robert McCullough, M.D.
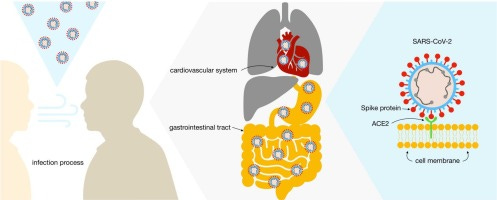
Spike protein is found in the myocardium, causing sudden death after vaccination with mRNA COVID vaccination. It is also found in the GI tract and other organs. Does spike protein make more viral particles?
Last month, our study titled, Excess Cardiopulmonary Arrest and Mortality after COVID-19 Vaccination in King County, Washington, was officially published in the Journal of Emergency Medicine: Open Access:
The relationship between the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, particularly from vaccines or infection, and myocarditis has been an area of growing research interest. Here are some key findings from recent studies:
Myocarditis and Vaccine Spike Protein: Cases of myocarditis following COVID-19 mRNA vaccination are rare but have been reported, especially in younger males. Studies have detected circulating spike protein in individuals who developed myocarditis post-vaccination, while such proteins were not present in healthy, vaccinated individuals. This suggests that the spike protein might act as a biomarker of inflammatory responses, though its exact role—whether causal or a consequence of inflammation—is unclear. This is supported by findings showing persistently elevated levels of the spike protein and associated inflammatory cytokines in these cases【18】【19】.
Spike Protein-Induced Cardiac Responses: Research on cardiac fibroblasts has demonstrated that the spike protein can activate pathways such as the NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB signaling. These pathways are associated with inflammation and fibrotic changes in the heart, which may underlie some of the cardiac effects seen during SARS-CoV-2 infections or after vaccination【19】.
Autoimmune Mechanisms: Some evidence points to autoimmune processes being a potential contributor to vaccine-induced myocarditis. Cross-reactivity between spike protein antibodies and myocardial proteins, as well as excessive CD4+ T-cell infiltration in affected patients, suggests that autoimmunity might drive some inflammatory responses in the heart【20】.
Infectious vs. Non-Infectious Inflammation: In cases of myocarditis following vaccination, evidence of direct infection was absent, ruling out viral myocarditis. Instead, inflammatory and autoimmune mechanisms, potentially initiated by spike protein exposure, seem to play a central role【20】.
Is Spike Protein found in other organs?
Heart and Blood Vessels: Inflammation in the endothelium (lining of blood vessels) and heart tissue has been linked to the spike protein's presence, potentially contributing to cardiovascular complications like myocarditis or blood clot formation.
Gut: Long-term presence of spike protein and viral RNA has been observed in gastrointestinal tissues. This persistence is associated with ongoing inflammation, possibly explaining symptoms like prolonged digestive issues.
Kidneys, Liver, and Spleen: Research has indicated that spike protein can accumulate in these organs, sometimes impairing their function or causing localized inflammation.
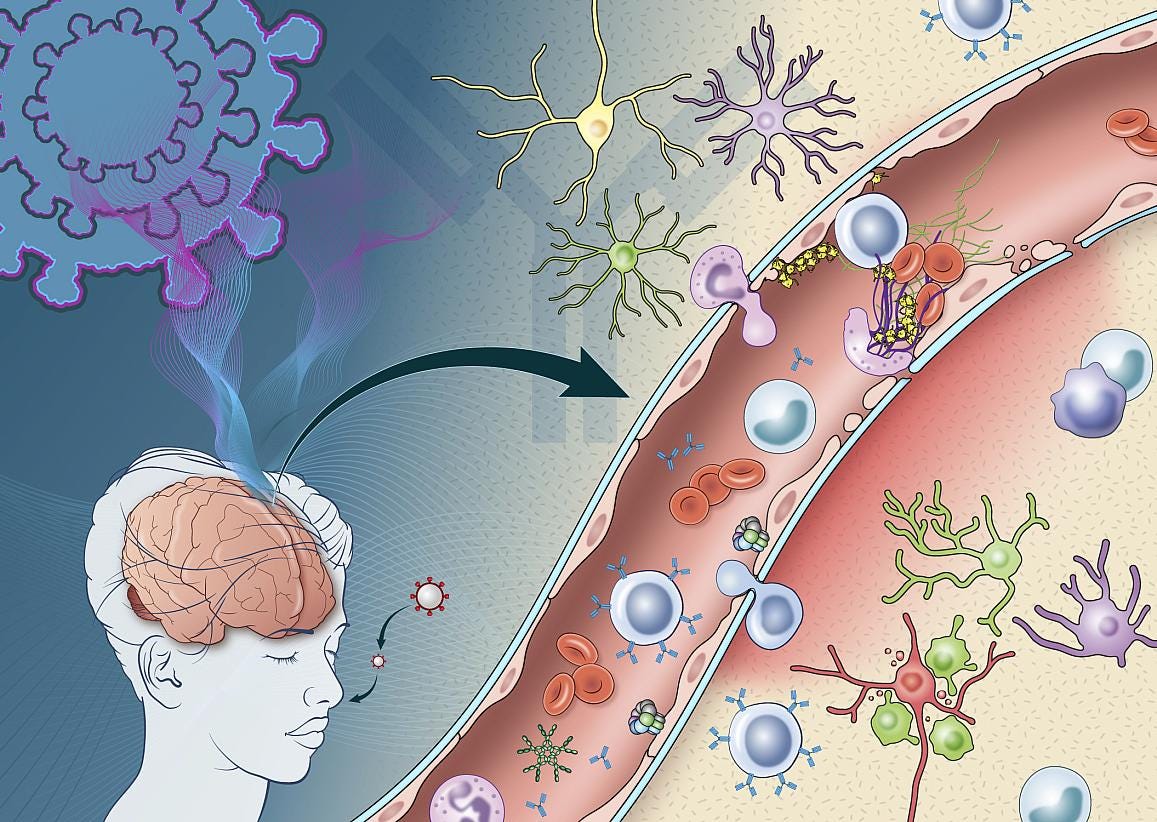
Immune System and Circulatory Cells: Spike protein fragments have been detected in circulating immune cells and blood for months after the acute phase of infection, suggesting viral persistence may drive chronic immune activation.
The presence of spike proteins in these vital organs may point to the multitude of post-COVID-19 signs and symptoms.
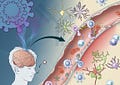
CNS Is Spike protein found in the CNS?
CNS spike Protein CNS Spike Protein (NIH study)
Clusters of spike protein are found in multiple organs.
mRNA technology is now being used to produce new vaccines, such as H1N51, and ZIKA. Clinicians must consider the etiologies of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in post-vaccination patients.
Peter McCullough MD sounded these warning bells in 2021, he was censored by the AMA and most other medical groups.
c